Helicobacter Pylori And Cancer: Are They Linked?
Stomach infections cause symptoms such as vomiting and abdominal pain. However, there is a gut bacteria that appears to be linked to cancer.
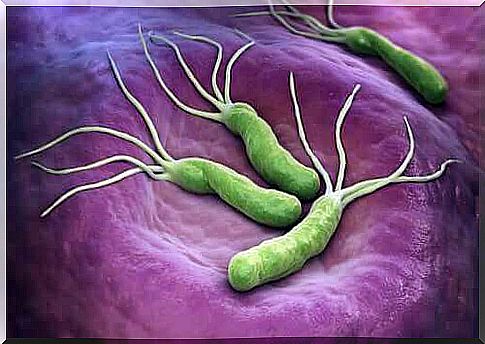
The relationship between Helicobacter pylori and stomach cancer is being researched in medical science because the prevalence of this bacteria in humans is high. What would happen if the microorganism were an oncological risk factor?
Symptoms such as stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting can be indicative of gastritis, and gastritis has different causes. One of them is the presence of the bacteria Helicobacter pylori in the digestive tract. Prevalence studies estimate that over 70% of infections with this microorganism are asymptomatic.
This bacterium is a puzzle for researchers, because besides gastritis and peptic ulcers, it seems to be linked to some kind of cancer. Is this bacteria so dangerous? In this space, we give you the answer to this question.
Helicobacter pylori bacteria
Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative bacterium in the form of a helical bacillus. It lives in the human gastric epithelium, that is, inside the stomach.
The bacteria are about three microns in size and have four to six flagella, which allows them to move around freely. She is microarophilic, so she needs oxygen for her survival, albeit at low concentrations.
Each human population has characteristic strains of H. pylori. This allowed scientists to estimate the migratory patterns of humans in ancient times, showing the relevance of the microorganism and its presence since time immemorial.
How is it transmitted and spread?
This bacteria has been isolated from fecal and oral samples from infected patients, so it is suggested that the most common mode of transmission is kissing or oral contact. It is a microorganism that we acquire at an early age, due to its large geographical distribution.
In some parts of the world, the fecal-oral route is the one chosen by the bacteria to spread. The consumption of water infected or contaminated by waste, is a simple way of entry.
What is the relationship between Helicobacter pylori and cancer?
In addition to causing gastritis and ulcers, this microorganism appears to be linked to mucosal associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (MALT), a type of gastric adenocarcinoma. Its symptoms are general, such as weight loss, anemia, discomfort and abdominal pain.
Revealing studies
Long-term infection with this bacterium appears to be positively related to the presence of gastric adenocarcinomas. A study that analyzed 17 populations from 13 countries showed that there was six times the risk of gastric cancer in people who had the bacteria than in those who did not.
Besides the spatial variation, there is an important temporal component. In the follow-up of 1225 Taiwanese patients, it was observed that after 8 years of surveillance, 2.9% of them with Helicobacter pylori developed gastric cancer, while no cases were observed in uninfected people.
However, these trends are not as clear in other parts of the world. For example, in Africa, it has not been possible to demonstrate a clear correlation between cancer and the presence of the microorganism.
How does this relationship come about?
Several hypotheses have been proposed in an attempt to explain the exact correlation between H. pylori and gastric cancer, but its mechanism of action has not yet been fully understood. The possible interactions are as follows:
- This bacteria causes damage to the gastric mucosa, resulting in damage to the epithelial surface of the stomach. DNA is damaged and protective factors such as vitamin C are reduced.
- The damage promotes cell proliferation, because damaged cells must be replaced.
- Bone marrow-derived cells that differentiate into gastric cells in the presence of H. pylori are said to be the most likely to become cancerous. This hypothesis is called the theory of bone marrow cell migration.
The exposed mechanism is a possible explanation, a hypothesis, but not definitive. The interactions between this bacteria and various health problems are still being studied.
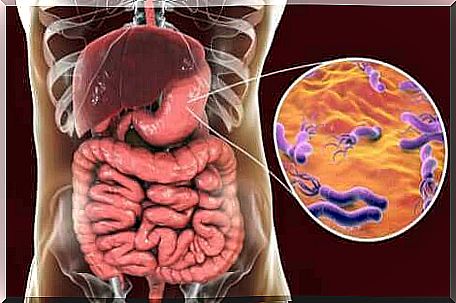
Helicobacter pylori and cancer: what to remember?
If it is estimated that two-thirds of the world’s population have been infected with this bacteria, we can magnify the problem and research concerns. Over 70% of infections are asymptomatic, so the risk of cancer from this microorganism may go unnoticed.
In cases of ulcers and other conditions, H. pylori can be eliminated with the use of antibiotics such as amoxicillin. It is therefore important to go to the doctor in case of suspicion, because good prevention is always the best option.