Vegetation Or Adenoiditis In Infants: Symptoms And Treatment
Adenoiditis is a common condition in newborns and children because the inflamed tissue disappears in adulthood. The most common cause of the disease is a bacterial infection.
Adenoids or adenoiditis in babies is a condition that is characterized by an increase in the size of the adenoids (mass of lymphoid tissue near the nostrils) relative to the size of the nasopharynx, resulting in nasal obstruction and various complications. According to pediatric sources, the general cause is an infectious episode.
Adenoids present a very characteristic symptomatology and are relatively common in children. Nevertheless, knowing when to go to the doctor and consider possible treatment is essential in these cases. That’s why here we tell you everything you need to know about adenoiditis in babies.
Who suffers from adenoids?
Before getting to the heart of the matter, we will describe the population group most likely to suffer from this condition. Various medical examinations provide us with certain data. Here they are :
- The prevalence of adenoids or adenoiditis in babies is difficult to quantify, as it is usually associated with other clinical conditions, such as rhinosinusitis.
- The highest morbidity (probability of onset of the disease), according to scientific studies, is between one and nine years.
- Adenoid tissue begins to atrophy from the age of 6-7 years and continues to decrease in size during puberty. That is why it is a characteristic disease of babies and children.
As we have seen, we are faced with a pathology biased by the patient’s age. In the face of symptoms of nasal obstruction in adults, adenoiditis is not considered to be one of the main causes.

What is adenoiditis?
As we have already said, this pathology corresponds to swelling of the adenoid tissue, a plaque located just behind the nose and which is part of the lymphatic system. This structure responds to infections by trapping germs and bacteria so that they do not enter the upper respiratory tract.
Adenoids are functional in infants and children, but according to the sources cited above, they reach their maximum size by the age of seven. From then on, they begin to decrease to the point of being almost absent in adulthood. Indeed, with age, people develop new immune mechanisms.
It is necessary to emphasize the difference between acute and chronic adenoiditis, although this concept does not appear to be standardized by all bibliographic sources. Adenoid tissue may become inflamed temporarily in response to an infectious episode, which is to be expected, but if the adenoids become infected, the clinical picture may become chronic.
According to the United States National Library of Medicine, infections are generally the most common cause of acute adenoiditis, although allergic processes or irritation from stomach acidosis may play an important role in its appearance. The bacteria most associated with this clinical picture are the following:
- Haemophilus influenza
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Staphylococcus aureus
Finally, it should be noted that repeated adenoiditis leads to adenoidal hypertrophy. In this case, it may be necessary to surgically remove the tissues, as their size will not decrease after infection.
Symptoms of adenoiditis in infants
Pediatric portals, such as Kidshealth , record symptoms of the disease in infants and children. Here are some of the most common signs:
- Dry mouth and bad breath
- Chapped lips
- Runny nose
- Ear problems
- Noisy breathing
- Recurrent nasal or sinus infections
All of these symptoms are caused by the inability of the newborn to breathe properly. When the tissue ignites, it blocks air from entering the upper respiratory tract, so the baby has to breathe in the mouth.
How is adenoiditis treated in babies?
The key to treating adenoiditis or adenoids in babies is to watch and wait. There is no point in giving antibiotics to a newborn baby who has an allergic reaction, so it is always out of the question to take the initiative and diagnose the patient ourselves. The pediatrician can take various measures:
- In the case of infections of a viral nature, no treatment is usually necessary. This type of upper respiratory tract pathology usually resolves after 5-7 days, according to scientific sources.
- In the case of bacterial infections, antibiotics can be used. Amoxicillin is one of the most widely used drugs and usually signals an improvement in the patient’s symptoms within 48 to 72 hours.
- If an allergic reaction is suspected, nasal steroid sprays or antihistamines are the solution.
- If heartburn is refluxing, changes in the infant’s diet and advice from a pediatric nutritionist should be sufficient to alleviate symptoms.
Again, if the patient does not respond to treatment and continues to be unable to breathe, making life difficult for them, an adenoidectomy, that is, removal of the adenoids, may be required. Most infants have no risk associated with this surgical process.
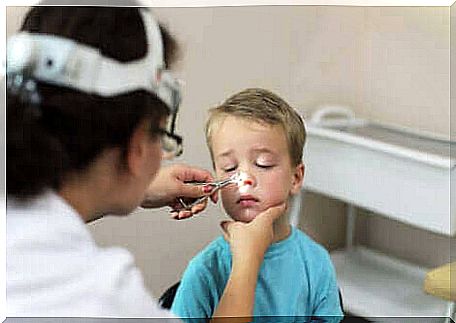
The role of the pediatrician
Adenoiditis is a very common disease that is often associated with other pathological processes of the upper respiratory tract. When a baby has difficulty breathing, halitosis, dry mouth, crying and continued discomfort, a visit to the pediatrician is necessary due to possible adenoids.
In addition, it should be mentioned that the episodes caused by bacterial infections also occur with the symptoms of these pathologies, that is, malaise and fever. Therefore, in case of any of these symptoms, a visit to the doctor is essential.