Burning Mouth Syndrome
Burning mouth syndrome is a disease characterized by a burning sensation in the oral mucosa, accompanied by dryness and taste changes. How to recognize it? What is his treatment?
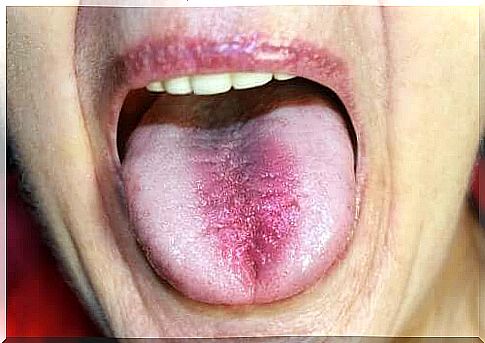
Burning mouth syndrome, also called glossodynia, is a condition characterized by xerostomia in women over the age of 50.
The saliva is a fundamental element in maintaining oral health because it is the natural lubricant oral tissues. It is also fundamental for digestion because it is this which forms the food bolus. Finally, it prevents the proliferation of conditions such as cavities or periodontal disease.
What is xerostomia?
This is the decrease in salivary flow at rest. It is more common from the age of 50, especially in women due to hormonal changes.
Furthermore, it may be a transient illness, associated for example with a state of anxiety, an infection, among others. But it can also be permanent and linked to the consumption of alcohol, tobacco, chemotherapy, etc.
What is burning mouth syndrome?
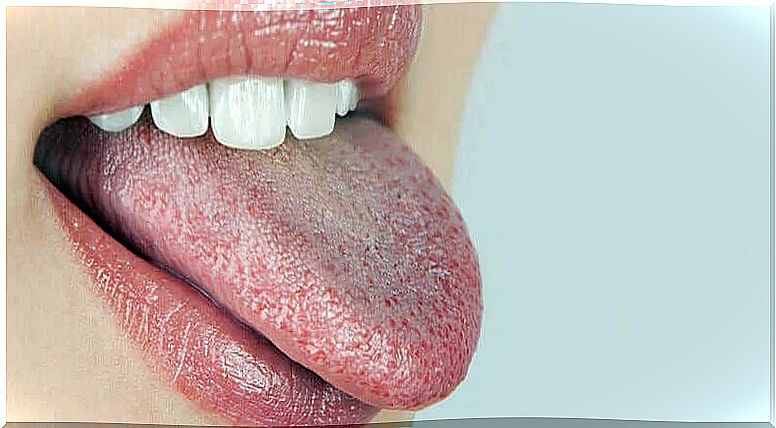
As we mentioned before, this is a pathology that is characterized by xerostomia. Mainly in women from the age of 50. Usually it is associated with hormonal changes, such as menopause. It is three times more common in women than in men.
In this syndrome, patients also present with dysgeusia. In other words, difficulty swallowing. Hyposalivation is closely linked to gingivitis, cavities or bad breath. The saliva then becomes thicker and dense. The mucous membrane is dry, irritated and red. Often the person exhibits the following symptoms:
- Burning in the mouth and on the tongue.
- Chapped lips.
- Dry mouth.
- Presence of ulcers.
- Constant thirst.
- Increased tartar build-up.
Symptoms usually increase in the evening and at night. Some patients also report a metallic or bitter taste in the mouth. On the other hand, it is very common for cavities to appear in the area of the neck of the teeth, at the root, due to the reduction in natural autolysis produced by saliva.
What is the treatement ?
If the cause is peripheral, in other words associated with drugs or other pathologies, the syndrome will disappear when the cause disappears. On the other hand, if there is no external cause, the treatment will be directed towards an increase in saliva in order to avoid the side effects of hyposalivation.
Dietary and health advice is generally prescribed to induce greater production of saliva. Often, to increase salivation, saliva stimulants are used in combination with saliva substitutes. We normally find them in the form of a spray , toothpaste, or mouthwash.
Can we prevent burning mouth syndrome?

To prevent this pathology, or remedy its symptoms in a natural way, you can take into account the following recommendations:
- Try to lead a more relaxed life, reducing stress.
- Increase the intake of fluids in the diet, making sure to drink about two liters of water every day.
- Try different soft toothpastes, without too strong a menthol flavor.
- Avoid the consumption of liquids and acidic foods, carbonated drinks or coffee.
- Avoid cinnamon.
- Decrease or reduce alcoholic beverages, as well as products containing alcohol.
- Remove spices from the diet.
- Eliminate smoking or reduce it as much as possible.
To summarize…
It is important to see a doctor whenever you notice changes in the amount of saliva, irritation of the mucous membrane, or any other symptom that lasts over time.
Finally, it is not only a question of treating the symptoms, but also to rule out other possible pathologies such as diabetes mellitus or a type of tumor. The doctor or dentist can then identify any possible causes of the disease and then treat it.