Penicillin Allergy: Types And Diagnosis
The classification of allergic reactions to penicillin is based on the time interval between the administration of the drug and the onset of the reaction. What do I need to know?
Penicillin is an antibiotic derived from the fungus Penicillium , which belongs to the group of beta-lactam antibiotics. There are different types of penicillins, but they all have the beta-lactam nucleus. However, each type of penicillin works differently against bacteria.
In addition to removing bacteria that cause various infections from the body, penicillin is used to prevent infections caused by gram-positive bacteria. What are the different types of penicillin allergy?
What is penicillin allergy?
Beta-lactam allergy is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. The diagnosis of penicillin allergy is made based on the clinical history and skin tests.
Types of allergic reactions
The classification of allergic reactions to penicillin and, in general, to beta-lactam antibiotics, is based on the time interval between administration of the drug and the onset of the reaction.
Immediate allergic reactions
These are reactions that take place within the first hour after administration of the drug. They usually occur because of specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) which releases histamine and other inflammatory mediators very quickly.
The form in which they appear varies from mild reactions such as hives, angioedema or wheezing, to severe reactions such as anaphylactic shock.
Accelerated reactions
This type of reaction occurs between 2 and 72 hours after the administration of the antibiotic. Although their mechanism is not well described, there may be reactions of urticaria, angioedema, laryngeal edema and wheezing.
Late allergic reaction
These are reactions that occur more than 72 hours after administration of the drug. They are usually mediated by T cells and manifest in a variety of ways.
Both accelerated and late reactions can be grouped together under the term non-immediate reactions. Some of the signs and symptoms of non-immediate reactions include the following:
- Maculopapular rash or morbiliform rash.
- Urticaria.
- Erythema multiforme.
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis.
- Exfoliative or contact dermatitis.
- Hypersensitivity syndrome.
- Lichenoid dermatosis.
Fortunately, the most common reactions are usually not serious and consist of a maculopapular rash followed by hives.
How do you diagnose a penicillin allergy?
If hypersensitivity is suspected, it is essential to have penicillin allergy examinations. This is essential, as side effects are often mistaken for allergic reactions.
Diagnosis is based on the description of the symptoms and the time between taking penicillin and the onset of the reaction.
Therefore, the type of allergic reaction can be classified as immediate or not immediate. In immediate allergic reactions, it has been found that the more time elapses between the initial reaction and the test, the less chance there is of finding a positive skin test.
However, this loss of sensitivity is not always present. Cases of new sensitization to these antibiotics are possible after a skin test or the repeated intake of the drug. On the other hand, in the case of non-immediate reactions, the phenomenon of loss of sensitivity is not usual.
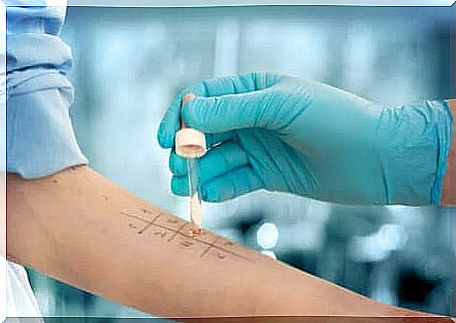
Skin tests to diagnose a penicillin allergy
For immediate reactions, we start with a prick test or skin allergy test. It is possible to use one or more criteria and, if the answer is negative, the next step is to perform an intradermal test.
Both are usually done on the forearm and the reading is done after 15 or 20 minutes. However, in case of non-immediate reactions, it is possible to start directly with the skin test with readings after 20 minutes, after 48 hours and after 72 hours.
Systemic reactions can occur during intradermal testing . This is especially the case when there are a lot of substances used at the same time.
Desensitization
Desensitization consists of re-administering the antibiotic causing the allergic reaction, in progressive doses, until the therapeutic dose is reached.
This process is reversible and depends on the continued presence of the antibiotic in the body. It therefore loses its effectiveness when we stop the administration of the drug for a period of more than 48 hours.
Conclusion
The penicillin antibiotic group is commonly prescribed. Therefore, in sensitized people allergic reactions occur and can be fatal.
This is why it is essential to correctly and precisely diagnose real allergies to antibiotics.